
I agree Our site saves small pieces of text information (cookies) on your device in order to deliver better content and for statistical purposes. You can disable the usage of cookies by changing the settings of your browser. By browsing our website without changing the browser settings you grant us permission to store that information on your device.
Development and Growth disorders are usually investigated for lethal or subviable mutations; this occurs for 24% and 10% of the genes, respectively (IMPC data). These genes are of special interest for both developmental biologists and clinicians as they are potential candidates for human developmental disorders and rare genetic diseases.
See our Anatomopathology dedicated page to explore all our available tests.
Cell death by apoptosis can be investigated in ex vivo sections by TUNEL staining (Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP Nick End Labeling) and/or cleaved caspase 3 immunohistochemistry. TUNEL represents the standard assay for detecting apoptotic cells on histological sections.
 Apoptotic granulosa cells (green dots) in atretic ovarian follicles
Apoptotic granulosa cells (green dots) in atretic ovarian follicles
When comparing apoptosis between different tissues, all samples are fixed and processed under the same conditions. At least, 3 mutant mice versus 3 littermate control mice are required for relevant results.
Tissue cell proliferation markers provide information on cell cycle progression with BrdU as an indicator of cells having passed through S-phase, phospho-H3 for cells in M-phase, and Ki67 for actively cycling cells.
 Detection of BrdU incorporation in seminiferous tubules: positive cells are confined to the periphery of the tubules and correspond to spermatogonia and preleptotene spermatocytes close
Detection of BrdU incorporation in seminiferous tubules: positive cells are confined to the periphery of the tubules and correspond to spermatogonia and preleptotene spermatocytes close
 Immunoperoxidase staining for detection of phosphorylated histone H3. Ventral prostate. Negative image obtained by Photoshop® processing of the original, dark-field, pictures. The labeled cell is in metaphase.
Immunoperoxidase staining for detection of phosphorylated histone H3. Ventral prostate. Negative image obtained by Photoshop® processing of the original, dark-field, pictures. The labeled cell is in metaphase.
 Immunoperoxydase staining for detection of the Ki67 (left panels) and DAPI counterstain (right panels). Stages VII (top two panels) and X (bottom panels) of the seminiferous epithelium cycle.
Immunoperoxydase staining for detection of the Ki67 (left panels) and DAPI counterstain (right panels). Stages VII (top two panels) and X (bottom panels) of the seminiferous epithelium cycle.
To better characterize the primary defects of the mutants, vascular (PECAM), neural (neruofilament), endodermal (HNF3b) markers are proposed. Other marker stainings can be developed on demand.
HREM is an effective and powerful tool for assessing structural abnormalities in embryos. Three dimensional reconstruction of embryo slices provides the definition of histological staining with the completeness of 3-D imaging.
HREM imaging is operated with a home made system (developed with the IGBMC Imaging Center)

1-The sample is fixed in Bouin’s solution
2-JB4 Resin embedding :
3-Samples limitations: the size must not exceed 1.5 cm3


It is recommended to use at least 3 experimental and 3 control samples for analyse.
Rapid three dimensional imaging of density-contrasted tissues (soft tissues) and non-contrasted tissues (skeletal elements) in the embryo using X-ray transmission and computed tomography.

The phenotyping of fetuses at later stages (E18.5) can use micron-scale X-rays Computed Tomography (μCT), which achieves a resolution of 10μm (isotropic voxel size) and allows the morphological analysis of organs in situ without dissection. To achieve sufficient contrast, formalin-fixed fetuses will be stained in Lugol’s iodine as a contrast agent. The impregnation of iodine in tissues will increase X-rays absorption due to iodine’s high atomic number and therefore enhance contrast in the resulting images. Obtained raw data have to be processed to facilitate direct comparison between samples.

It is recommended to use at least 3 experimental embryos and one control embryo for analyse.
Sampling of embryos for viability at times throughout pregnancy with focus on development of particular organs between E9.5 and E18.5.
 Determination of the window of lethality
Determination of the window of lethality
Embryonic growth restriction can be indicative of placental abnormalities. Macroscopical and routine histological analysis (hematoxylin & eosin) are performed to evaluate placental defects.
Rapid three dimensional imaging of density-contrasted tissues (soft tissues) and non-contrasted tissues (skeletal elements) in the embryo using X-ray transmission and computed tomography.
The phenotyping of fetuses at later stages (E18.5) can use micron-scale X-rays Computed Tomography (μCT), which achieves a resolution of 10μm (isotropic voxel size) and allows the morphological analysis of organs in situ without dissection. To achieve sufficient contrast, formalin-fixed fetuses will be stained in Lugol’s iodine as a contrast agent. The impregnation of iodine in tissues will increase X-rays absorption due to iodine’s high atomic number and therefore enhance contrast in the resulting images. Obtained raw data have to be processed to facilitate direct comparison between samples.
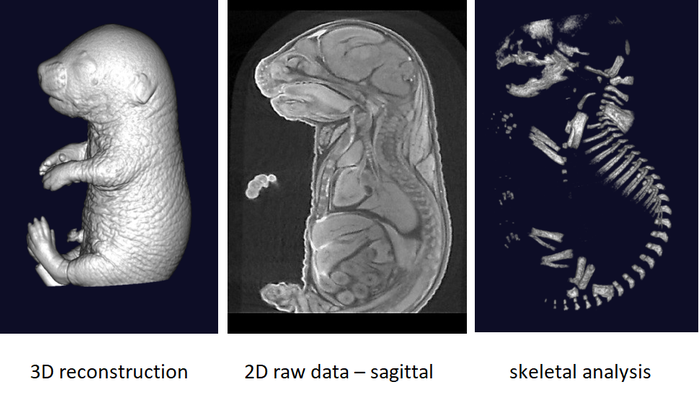
It is recommended to use at least 3 experimental embryos and one control embryo for analyse.
The measurement of various blood metabolites, ions, and enzymes provides a primary screen for function of major metabolic organs such as kidney, liver, gastrointestinal tract, as well as for lipid and glucose homeostasis.
A panel of parameters is proposed, including:

Selected plasma chemistry data from female mice (N=20 per line) of common laboratory strains at different ages (Champy et al. Mammalian Genome 2008). Error bars reflect ± SEM.
These tests are performed with an AU-480 automated laboratory work station (Beckman Coulter France SAS, Villepinte, France).
Body composition for fat, lean and free body fluid is evaluated on conscious mice by quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance on Minispec analyzer.

Body composition analysis of male mice from different common laboratory strains after provision of chow diet (CD) or 10 weeks provision of high-fat diet (HFD), including complete body weight, fat tissue content, and lean tissue content. Dramatic increases in fat tissue is seen upon HFD-diet treatment for most strains excepting BALB/c, consistent with what has previously been reported.

Body composition is evaluated by Quantitative Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (qNMR) using Minispec+ analyzer (Bruker BioSpin S.A.S., Wissembourg, France)
First-line hematological/immunological analysis of blood or tissue infiltrates for different leukocyte lineages. May be targeted to examine particular immune lineage subclasses.
Exemples:
Thymus:
Spleen:
Blood:
Please see our Immunology dedicated page for more detailed tests.
FACS analysis are performed on a LSR II (BD diagnostics, Le pont de Claix, France).
See our Gene expression analysis dedicated page to explore our different related tests.
See our In vivo Viral Transduction dedicated page to explore our frequently used vectors and delivery modes including stereotactic admininistration (intraventricular and cerebellar)
With several months notice, we can procure and provide a variety of different restriction diets for nutritional analyses in conjuction with our other analyses.
The X-Ray system gives very precise images of the skeletton. In DXA mode it automatically calculates BMD, BMC, and lean and fat mass percentages.

pDEXA Sabre (Norland)
With several months notice, we can procure and provide a variety of different restriction diets for nutritional analyses in conjuction with our other analyses.
See our In vivo Viral Transduction dedicated page to explore our frequently used vectors and delivery modes including stereotactic admininistration (intraventricular and cerebellar)